What is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
SEO, or search engine optimization, is a digital marketing discipline that aims to help a website earn a greater volume of relevant visits from the unpaid, “organic,” results provided by search engines.
SEO helps companies connect with their target audiences by maintaining the brand’s presence in search results. It’s a major component of many digital marketing strategies.
Why is SEO Important?
A strong SEO strategy not only bolsters a brand’s online presence, it attracts and nurtures high-value leads, getting the right information in front of the right decision-makers at the right time.
87% of people turn to search engines first when they have a question or a need.
93% of all online experiences start with a search engine.
Whoever your buyer is—B2B or B2C—they’re looking for information about your product or service on the internet.
Additionally, about 200 million people worldwide use ad blockers, so organic results become even more important when reaching buyers. While paid search is a consideration for many marketers, it is by no means the best way to reach the most important part of your audience:
57% of B2B marketers say SEO has the biggest impact on lead generation.
Only 3% of searches result in a paid ad click. 62% result in an organic click.
How Do Search Engines Work?
Search engines use web crawlers and algorithms in order to show users helpful results:
Web crawlers (or spiders) constantly comb through the internet, storing and indexing the information they find.
Search algorithms sort through the information that web crawlers record, checking for a variety of characteristics, or ranking factors, that indicate a page provides the best version of the information that the user is looking for.
The sticking point for SEO is that not only do those ranking factors change depending on which search engine a person uses, but there can be hundreds of them.
Search algorithms—Google’s in particular—used to look at ranking factors such as how often a page contained users’ search terms and how many other pages linked back to it. But, over the years, Google changed the way it prioritizes ranking factors. Today, it elevates content that provides the best user experience and is most helpful to users, over content that may be technically “perfect” or stuffed with keywords.
Ultimately, it’s helpful to remember that search engines make their money from ad sales, and selling those spots at a premium requires a big user base. Creating and maintaining that user base requires creating an outstanding user experience. Thus, every update that Google makes is going to based on creating the best user experience.
How Does Modern SEO Work?
As Google’s algorithms have continued to advance over the years, the search engine has been able to switch out ranking factors that are easily manipulated for those that are better indicators of high-quality content and user experiences.
Modern SEO rises above a focus on algorithm updates and isolated ranking factors, to focus on Google’s end goal: a great user experience. Creating that competitive UX starts by understanding what a user needs when they type any relevant phrase into a search engine.
However, before marketers can take their SEO strategy to the next level with user needs, they need to make sure they’re addressing some foundational items.
SEO Basics
There are a couple of different types of optimization that SEO professionals need to lock down to ensure a page is, for starters, on par with the millions of other optimized pages online.
Here are some of the common terms that crop up in relation to those optimizations:
Keyword: SEO keywords are the terms and phrases marketers use to mirror search queries and connect their content with target audiences. They’re the common language between searchers and search engines. Today, more searchers are using long-tailed keywords—search terms that consist of three or more words.
Search volume: Search volume is the average number of times a keyword is typed into a search engine during a specified period of time, usually one month.
SERP: SERP stands for search engine results page. As the moniker suggests, a SERP is the page of links that come up when a person runs a search. The higher up on the SERP a page ranks, the more traffic it tends to get.
Featured Snippet: A featured snippet is a box that often shows up at the top of SERPs. Google pulls the most useful and relevant content off the page and incorporates it into the top of the SERP.
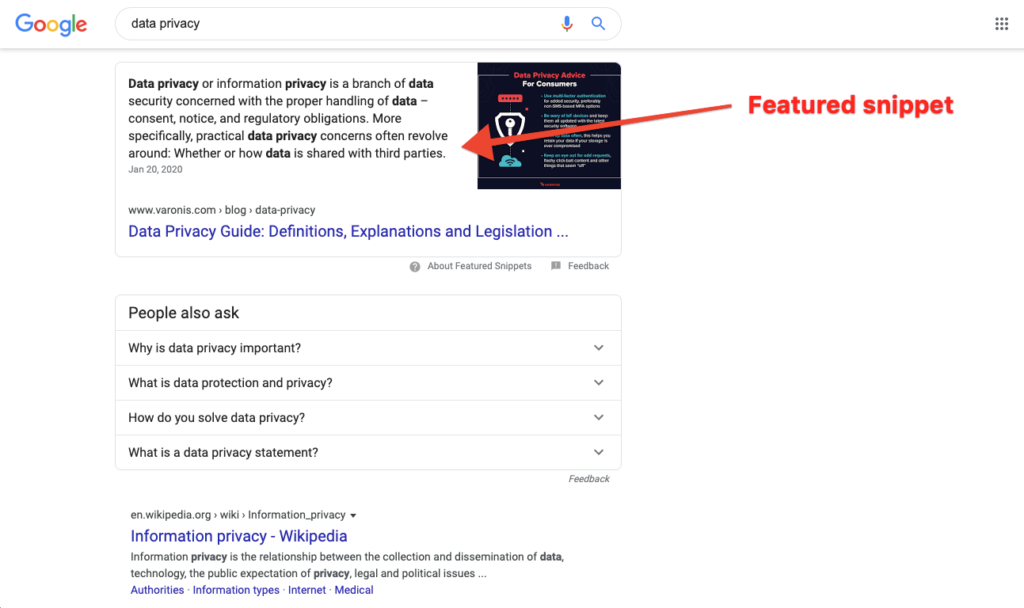
Because it appears before any actual search results, many marketers refer to the featured snippet as position zero. Like all rankings, the featured snippet changes as rankings change. However, a URL doesn’t need to be in the number one spot before Google will elevate it into the featured snippet.
Technical SEO Basics
Technical SEO is just one type of optimization a marketer will encounter. It typically includes tweaking back-end aspects of a website to improve UX and ensure Google and other search engines can easily crawl a site. Some action items might include:
Redirect broken links to lead users to the correct page, if there is one.
Limit page load times to three seconds or less.
Ensure crawlability (ability for Google to crawl your website content) and indexability (ability for Google to properly catalog your website content).
Optimize the website for mobile users (perform usability testing and look at mobile UX).

On-page SEO Basics
The other type of SEO is on-page SEO. As the name implies, it entails improving items that users can see on the page. Some of those items are:
Internal and external links that point to a site’s own content and authoritative, relevant elsewhere.
Meta descriptions that searchers see on a SERP.
Headings tags (H1, H2, H3) that format text as headlines and subheadings.
But perhaps most importantly, on-page SEO deals with the actual content users need. Crafting the best possible content that’s easy to read, engaging, and—most importantly—helpful to users, should be the main concern of modern SEO marketers.
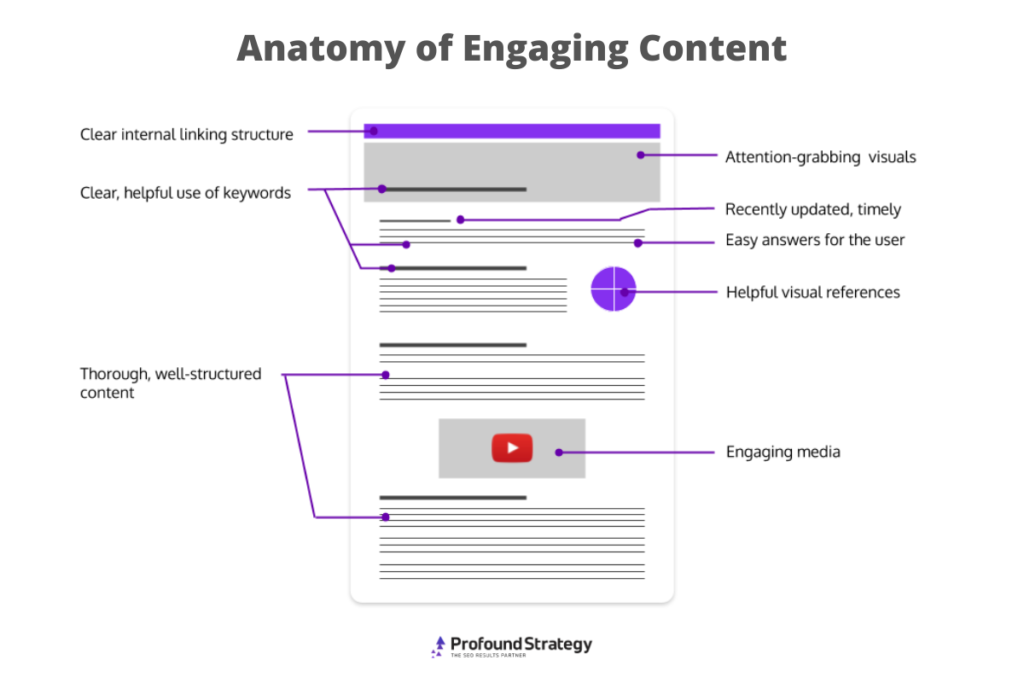
Writing SEO Content
While SEO basics remain fairly consistent over time, Google’s algorithm is always changing—and that has pretty big implications for how marketers create SEO content.
In order to create content that ranks well and drives organic traffic no matter how often the algorithms change, smart marketers go beyond the basics in order to create better-than-best content. This process is centered on content that addresses a specific user need, not just a topic or keyword.
How to Learn More
SEO isn’t what it used to be, but it’s more important than ever. Search engines are constantly evolving, and to keep up, SEO strategies must evolve too.
On top of that, each minute, hundreds of websites are created and added to the ether that is the internet. That’s a lot of content to compete with.
To learn more about how to create content that can survive and thrive in the ever-changing world of SEO, download our Modern Guide to High-Impact SEO Content or contact Profound Strategy today for a custom strategy tailored to your brand.
hbspt.forms.create({
portalId: “7076836”,
formId: “c205ac59-9e89-4abd-af83-b9d1c8512eb1”
});