11 Steps to Rockstar SEO
An effective SEO strategy is important.
91% of users turn to search engines for information.
75% of people never scroll past the first page of search results.
But you know that. The problem is, designing, creating, and maintaining an effective SEO strategy—one that actually improves organic rankings for important queries and drives qualified organic traffic—is hard.
SEO has rapidly evolved over the past few years and search engines are now running on machine learning algorithms. To further complicate matters, there are already hundreds—if not thousands—of existing posts and pages for almost any topic, and winning SEO means beating them all.
While the factors that impact rankings can climb into the hundreds, there are some key steps you can take to start improving your SEO today.
1. Translate SEO Keywords to User Needs
At its core, SEO is about connecting a target audience to an organization’s website at all the right moments. Presenting that audience with the information they need increases the chances they’ll interact with the site and, subsequently, can boost your rankings on a search engine results page (SERP).
That means that the most crucial step to creating relevant content begins with discovering what the user is looking for with each query or keyword on your list.
user need
n. – a specific need that a user has, at a specific point in the buyer’s journey, that inspires an organic search query
Start by studying Google’s results pages for those terms.
Examine organic results, and other Google features, on SERPs for related keywords, and determine what kind of user need Google seems to be addressing.
Do most of the results on the SERP provide a simple definition? Detailed instructions? Product pages? What question or need is Google trying to answer?
Be aware that a keyword can have multiple user needs, and that different keywords can correspond to the same user need.
For instance, maybe for one keyword’s SERP, half of the URLs seem to be product pages, while the other half compare one product to another. If that’s the case, there are multiple user needs aligned with that keyword: a need to find a specific product and a need to compare products.

Organic results for “workforce management” reveal two main user intents: “I need a definition of …” and “I need software for …”
Understanding this relationship between a keyword and the need(s) aligned with it will inform the direction your content should take.
2. Investigate Winning SEO Content
Identifying the users’ need(s) for target keywords is the first big step to improving a site’s SEO, but now you need to make sure that your content for any user need is better than everything else on the web for the same need.
That’s a big job.
Fortunately, Google has already done the heavy lifting of discerning what users prefer, and savvy marketers just have to learn to read between the lines. We do that by studying the content that is already winning organic search for a target user need.
Start by searching a few related terms and then analyze the top five organic results. Try to reverse engineer why Google prefers those pages. What are they all doing that users are evidently engaging with? You might be surprised at all the competitive insights you can glean.
Profound’s CEO explaining how modern SEO keyword research drives key insights you just can’t get any other way.
For more details on discovering user need and investigating top-performing content, see “How Certified Content Consistently Delivers ‘Better-Than-The-Best’ SEO Content.” →
3. Create Even Better Content
Once you finish researching, it’s time to create content.
The insights gathered from user need discovery and from studying top-performing organic content will inform the foundation of a competitive piece of SEO content. Then, build and improve upon that framework.
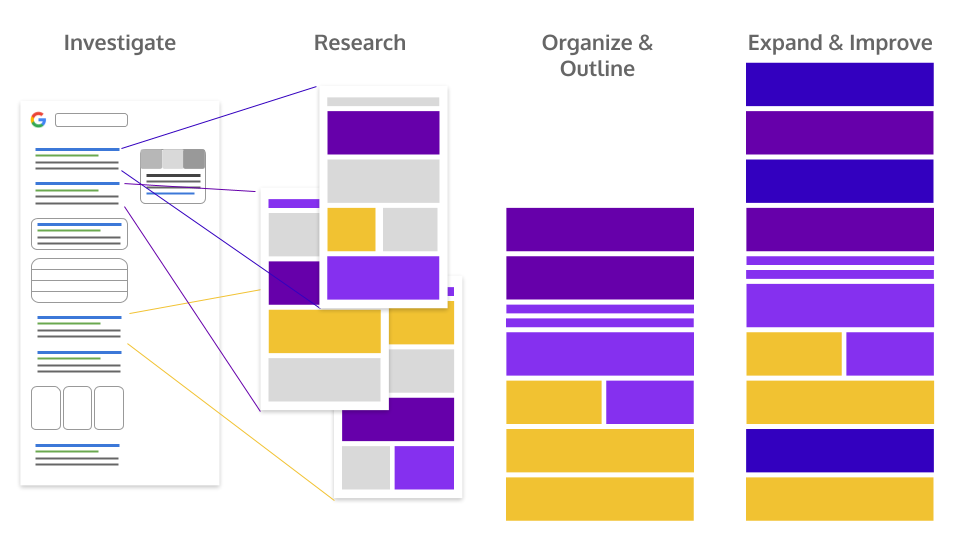
Once you’ve covered the basics, there are several strategies for expanding and improving a piece of content to make it really stand out:
- Highlight the brand’s unique voice, position, opinion, and insights.
- Contribute new/original research to the conversation.
- Combining subtopics and content elements from several top-performing pages into one complete content piece.
- Use short videos or custom diagrams to help explain concepts better than the competition.
Additionally, it’s important to realize that if a brand has multiple pieces of content that all target the same user needs, those pieces will fight for the same traffic and attention. Therefore, be sure there is only one piece of content per user need.
4. Analyze Content and Update Regularly
Researching and writing are non-negotiables, but it’s also impossible to keep a site fully optimized without tracking its performance.
Many companies turn to a variety of tools to facilitate this analysis. Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and other applications allow professionals to make data-driven decisions about how to upgrade content and make technical enhancements to a site.
Let’s suppose both tools indicate your URLs earn a high number of clicks from SERPs, but those pages are performing poorly in terms of bounce rate and time-on-page. This means that, though people are clicking on your URLs in the SERPs, no one is sticking around long enough to find other content on the site.
It’s likely that customers aren’t engaging with the site content because it’s not what they need, or there’s something hindering them from accessing the correct information.
Use this information to course correct. Perhaps the user need tied to that page’s main keywords has changed. In that case, another round of keyword research and SERP analysis can shed light on how to update that content.
Technical SEO Foundations
Better-than-the-best SEO content is how savvy digital marketers drive organic growth. While technical factors aren’t as important as they used to be, the right technical considerations can still make or break SEO efforts.
The key to good technical SEO is knowing when to stop. There are a few important tasks to take care of, but then it’s time to get back to creating outstanding SEO content.
5. Make it Mobile-Friendly
These days, web pages need to be mobile-friendly.
77% of executives use their smartphones to research a product or service for their business.
Roughly one-in-five U.S. adults rely solely on their smartphones for internet connectivity.
Given the trend toward mobile, Google has included a mobile-first index to their algorithm, favoring sites with pages responsive to smartphones and tablets. That means that mobile-friendliness isn’t just about mobile users anymore—it’s about rankings and traffic on every device!
Take the time to guarantee that users have a seamless and engaging mobile experience.
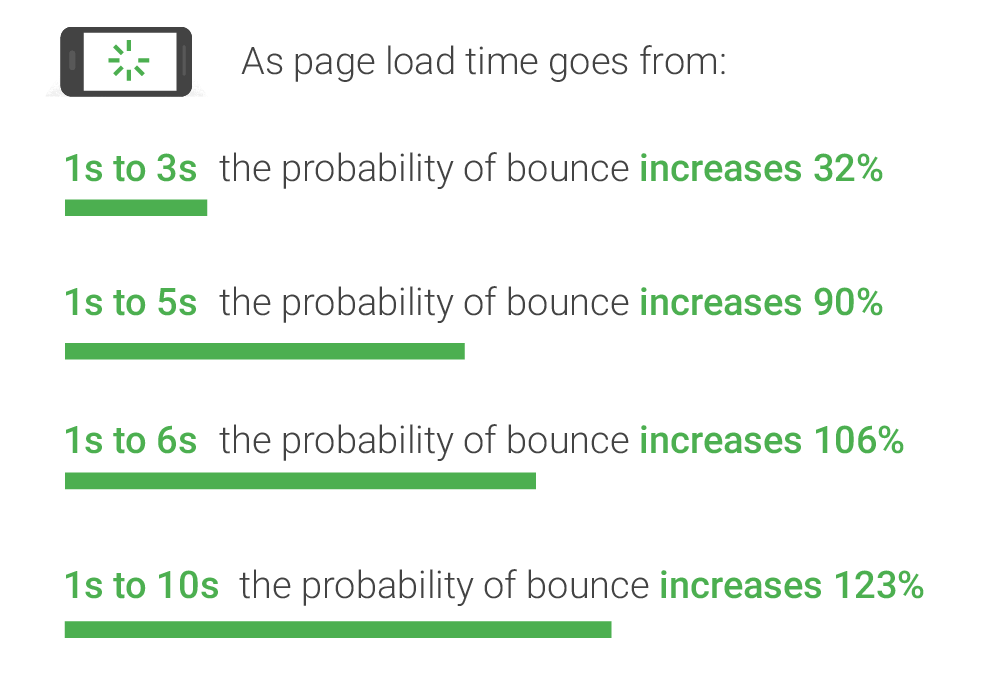
6. Make it Fast
A fast load speed—less than 2 to 3 seconds—is critical to retaining users. There’s a 90 percent chance users will leave if a page takes five whole seconds to load.
Slow pages frustrate users and dissuade them from staying on a site. In the mind of prospects, a slow site is an untrustworthy one. Consider utilizing a format like accelerated mobile pages (AMP) that remove clunky page elements that can slow down load times.
7. Make the Navigation Intuitive
Navigation is a major component of any website. It should be immediately obvious where to find important information such as how to order products or how to contact someone for help.
Plus, other navigational items like links and buttons should all work properly, leading users to the correct page that’s properly formatted for their device.
8. Make Sure the Site is Accessible to Search Engines
Algorithms dictate SEO rankings. If an algorithm can’t recognize a site, the SEO ranking will automatically decline. Remove any barriers, like too much duplicate content or issues with the sitemap, that might block crawlers from indexing the site.
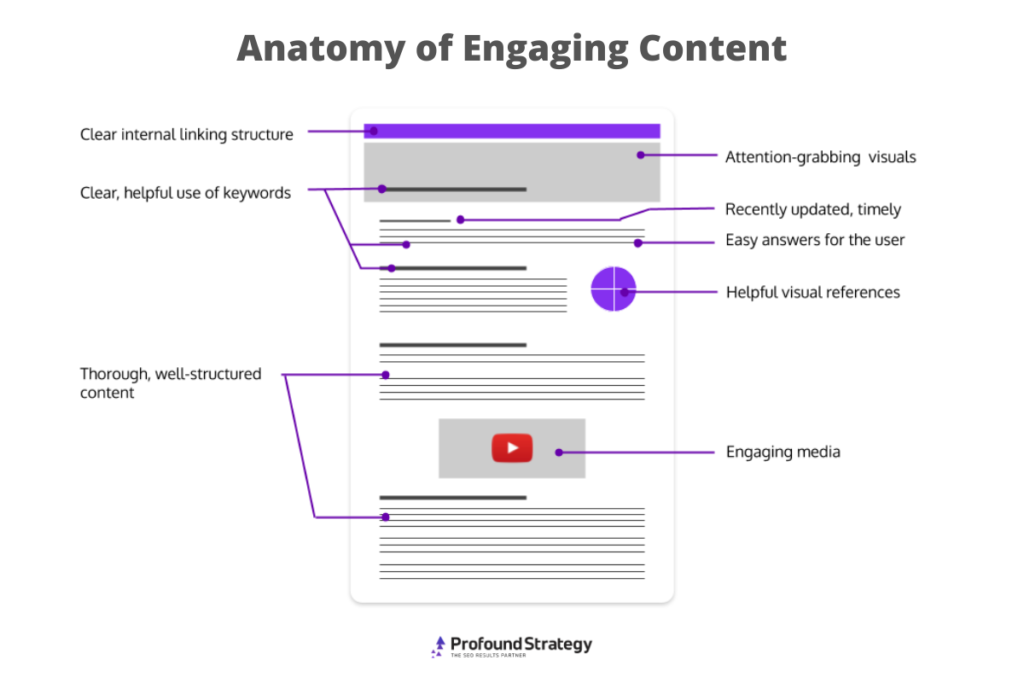
9. Optimize Images
Search engines favor visuals like graphs, pictures, and diagrams. Imagesㅡpreferably custom imagesㅡmake content more exciting and can lend credence to your authority.
Image Size
Large images can put a damper on load time, diminishing UX and SEO rankings. For example, the maximum upload size for WordPress is between 2MB and 150MB by default. If the image file sizes are too big, users can even receive a 500 Internal Server error.
Test out your images before publishing to verify that the size doesn’t detract from UX.
Alt Text and File Name
The primary function of alternative, or alt, text is to describe images to make them more accessible for users with visual handicaps.
Since Google and other search engines crawl alt text, many SEO professionals use it as an opportunity to incorporate target keywords. While this is a smart tactic, alt text should service the reader above all else. Incorporate keywords naturally, if they’re applicable, but focus on describing the image in a way that’s helpful to visually handicapped users.
Another way to make images work for your site is to include a descriptive file name. Google uses those file names to determine the image’s subject. Using a short name with hyphens between words makes it easier for search engine crawlers to detect the content of your image.
10. Optimize Your Content The Right Way
Finally, look at the content on the page. Does it look … nice? Is it easy to understand if you just scroll and skim headers and images? Does it translate to a mobile device well? It’s hard to quantify some of these considerations, but they’re all building the UX that’s driving the engagement metrics.
Use SEO-friendly Formatting
The internet is a big place with innumerable distractions. As such, users’ attention spans are short, and they want information they can consume quickly and easily.
Good web writing keeps this distractibility in mind, utilizing short paragraphs, bulleted and numbered lists, and links to useful, trustworthy sources—all of which helps readers find what they need easily.
Use Heading Tags
Break up content into easy-to-digest sections with header tags (H2, H3, etc.) that use keywords and phrases tied to a user need.
By formatting headlines and subheads with H tags, search engine crawlers can more easily identify what topics an article pertains to and why it’s relevant to users. Likewise, headers allow human readers to skim content much quicker to find the main points and decide if a page has value.
Use Keywords Strategically but Naturally
Google quickly realized that keyword stuffing was a loophole for stealing high organic rankings, and now penalizes pages for keyword stuffing—lowering organic rankings. So use keywords strategically, but never unnaturally.
Think about including keywords in places that help users and search engines easily understand content, such as:
- Heading tags
- The first few paragraphs
- Image titles and alt text
- Anchor text
But, again, never at the expense of the user experience.
11. Optimize Meta Text for CTR
Engaging content is rewarded with improved organic rankings. Content that ranks higher earns more engagement. Around and around it goes, so consider optimizing for SERP CTRs as well.
Keep SEO Page Titles Short and Compelling
SEO page titles are used by search engines to decipher content, and by users to decide whether or not to click. Convoluted titles, that force the reader to slow down and interpret, will likely lead to them skipping over the site in favor of a competitor’s.
Concise, compelling titles, on the other hand, attract people to a page and help them home in on their need.
Simplify URL Structure
Simple URL structure makes content easier to find, easier to share, and entices a user to click more. URLs that include keywords are easy to search and categorize. Clean, readable, and relevant URLs lend credibility to a site and enhance its search engine ranking opportunities.
Use Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are considered as 155-character summaries of a page’s content. Convince readers that your site has the specific information they are looking for.
Note, however, that Google is more and more frequently scraping text off the page to replace whatever we identify as the meta description. Google looks for text that answers the user need, so SEOs should craft meta descriptions with the user and competitive research in mind.
There should be a unique meta description for every page of a site. For instance, a meta description for a page about digital marketing should not have the same meta description as a page about customer service.
Start Improving Your SEO Today
Clearly, there are many important steps on the path to securing a top spot in the SERPs, the most critical of which is to create the best, most engaging content.
For even more details, don’t miss our CMO’s Guide to Modern SEO. This free ebook breaks down our framework for creating reliable SEO results, how to identify the SEO work that actually matters, and more
Or, to jump the curve and see how your organization can start attracting more organic traffic faster, contact Profound Strategy and talk to one of our search strategists about a customized SEO results campaign.


